Arduino Pro Mini Pinout, Pin diagram and specifications in detail
Содержание
- Arduino Pro Mini Pinout image:
- Arduino Pro Mini Pin diagram layout (official):
- Arduino Pro Mini Pinout details:
The Arduino Pro Mini is a microcontroller board based on the microchip ATmega328. The board consists of 6 analog inputs, 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), a reset button, an onboard 8Mhz resonator, and holes for mounting pin headers. A six-pin programming header can be connected to an FTDI cable or Spark fun breakout board to provide USB power and program the board. Atmega 328 based Arduino Pro Mini pinout and specifications are given in detail in this post.
There are two different versions of the Arduino Pro Mini: one runs at 3.3V and 8 MHz, and the other one at 5V and 16 MHz.
Arduino Pro Mini Pinout image:
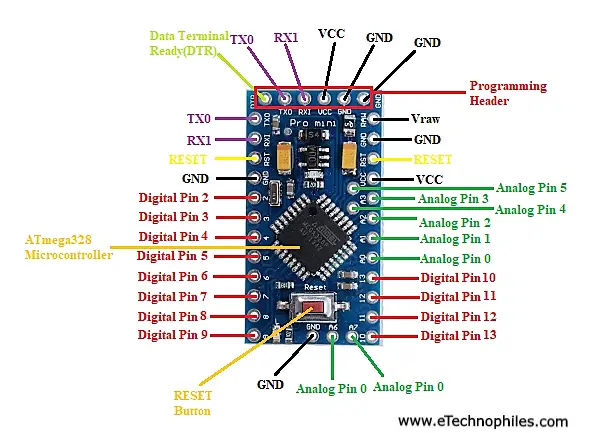
Arduino Pro Mini pinout
Arduino Pro Mini Pin diagram layout (official):
a) Mini 03 (older version)
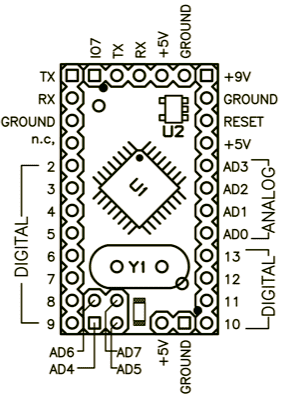
Arduino Pro Mini 03 pinout
b) Mini 04 and 05 (New version)
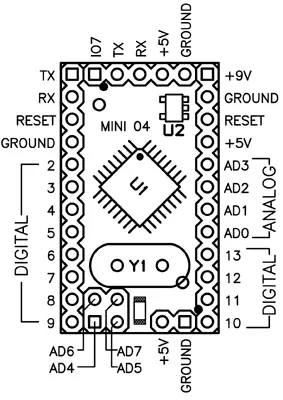
Arduino Pro Mini 04 / 05 pinout
NOTE: the ground on the left has moved down one pin.
Arduino Pro Mini Pinout details:
ATmega328 microchip:
The ATmega328 microcontroller is a high-speed, power-efficient AVR 8-bit microcontroller. It consists of 32 KB of flash memory for storing the program code (0.5 KB is used for storing the bootloader), 2 Kbytes of SRAM, and 1 Kbytes of EEPROM.
RESET Button:
This button generates a low-level signal at the pin which is used to reboot the microcontroller.
Arduino pro Mini Power Supply Pinout:
RAW: RAW is the input voltage that runs into the regulator. The supplied voltage at this pin can range anywhere between 3.4 to 12V.
VCC: It is the regulated voltage of 3.3V. We can change the voltage supplied voltage to 5V depending on the versions of the board.
GND: There are three GND (Ground) pins present on the Arduino Pro Mini board.
Arduino pro Mini Pinout – Digital Pins :
There are 14 digital I/O pins. The Arduino digital pins can read/output only two states: when there is a voltage signal and when there is no signal. This kind of input/output is usually called digital (or binary) and these states are referred to as HIGH or 1 and LOW or 0. These digital pins can be configured as an input or output using the pinMode (), digitalWrite (), and digitalRead () functions.
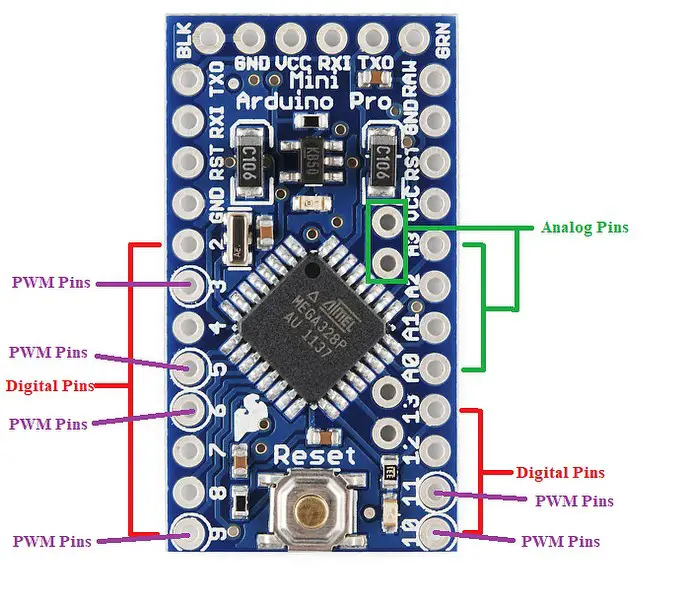
Digital, PWM, and Analog pins
Arduino pro Mini Pinout – PWM pins :
There are six pins from the set of digital pins that are PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) pins, numbered as 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11. Every one of these digital pins can generate a Pulse Width Modulation signal of 2 3 -bit resolution. We can generate the PWM signal using the analogWrite() function. Either pin provides 8-bit PWM with analogWrite ().

Arduino pro Mini Pinout – Analog Pins :
Arduino UNO has 6 analog pins, whereas Mini has eight analog pins numbered from A0 to A7. You can connect up to 8 analog/digital sensors to the board. The function of Analog pins is to read the value of the analog/digital input used in the connection. Each of these analog pins has an inbuilt ADC of resolution of 2 10 bits (so it will give 1024 values).
Note: Analog pins A4 and A5 are behind the Analog pins A2 and A3. These are placed in a tight spot to achieve a small form factor.
Serial bus (RX and TX):
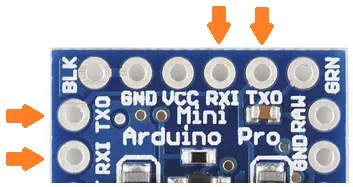
UART pins of Arduino Mini
These pins are used for serial communication. The pins are used to receive (RX) and send (TX) TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) data. These pins are connected to the TX-0 and RX-1 pins of the six-pin block of the board.
External interrupt (2 and 3):
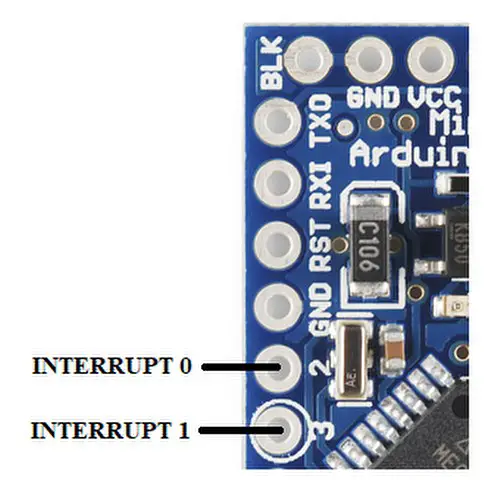
Interrupt pins of Arduino Mini
These pins can be used to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value.
SPI Pins on Arduino Pro Mini Pin diagram:
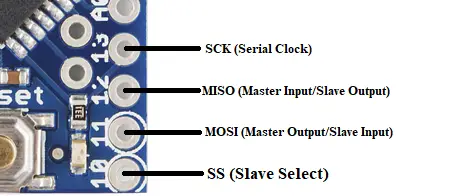
SPI pins of Arduino Mini
It stands for Serial Peripheral Interface. These pins are used by the board to communicate with one or more peripheral devices quickly. There are three common lines to all the peripheral devices:
- SCK-It stands for Serial Clock. These are the clock pulses, that are used to adjust the transfer of data.
- MISO-It stands for Master Input/ Slave Output. This data line in the MISO pin is used to send the data to the master.
- MOSI-It stands for Master Output/ Slave Input. This line is used for transmitting data to the peripheral devices.
- SS-It stands for Slave Select. This line is used by the master. It acts as the enable line. When a device’s SS pin value is set to LOW, it can communicate with the master. When it’s value HIGH, it ignores the master command. This allows us to have several SPI peripheral devices sharing the common MISO, MOSI, and CLK lines.
I2C pins on Arduino Pro Mini Pin diagram:
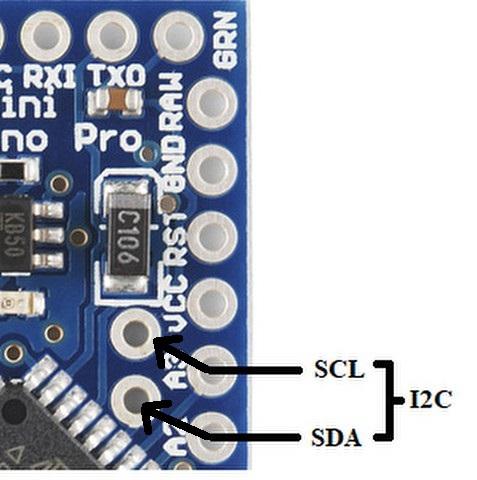
Arduino Mini I2C pins(A4 A5)
It is the two-wire serial communication protocol. It stands for Inter-Integrated Circuits. The I2C uses two lines to send and transmit data: a serial clock pin uses (SCL) and a serial data (SDA) (SDA) pin.
- SCL(A4)-It stands for Serial Clock. It is defined as the line that transmits the clock data. It is used to adjust the shift of data between the two devices. The Serial Clock is initiated by the master device.
- SDA(A5)-It stands for Serial Data. It is defined as the line used by the slave and master to send and receive data. That’s why it is known as a data line, while SCL is called a clock line.
LED: In the board, there is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When this pin is set HIGH or 1, the LED turns ON. When the pin is set LOW or 0, the LED turns OFF.
RESET: This pin is used to reset the microcontroller.
DTR (Data Terminal ready): This pin is used to reset the board and enter the bootloader for programming the Arduino pro mini board.
Источник:










